Key Takeaways
- compression stockings and tights are medical devices that exert pressure on the legs, improving blood circulation and relieving various venous disorders.
- The choice between stockings and tights will depend on preferences and lifestyle, with tights offering a greater compression surface.
- The compression class must be adapted to the severity of the symptoms: class 1 for benign disorders, class 2 for moderate venous insufficiency, class 3/4 for serious cases.
- It is essential to put on your stockings or tights correctly to optimize the benefits: put them on while lying down, smooth from bottom to top, avoid wrinkles.
- Compression stockings/tights are generally worn every day to optimally maintain blood circulation.
The French brand The Oversized Hoodie® 🇫🇷 is famous for its lined tights high-end, certified Oeko-Tex® Standard 100 and Oeko-Tex STeP. It is entirely vegan, free of toxic and chemical substances, and promotes a cruelty-free approach towards animals. These lined tights, which have also been honored with the “Confiance Textile” Quality Label, are distinguished by their incomparable softness and excellent value for money, providing an unrivaled feeling of comfort.
Understanding venous contention
What is venous restraint ?
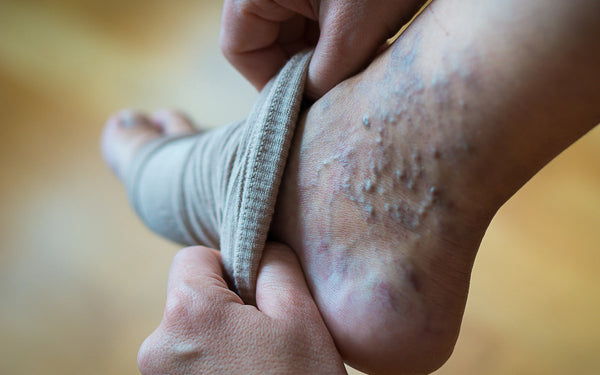
venous restraint refers to the use of devices exerting pressure on the legs, such as compression stockings, tights, or socks. The principle is to help venous return, that is to say the return of blood from the legs to the heart, fighting against venous stasis.
In fact, the pressure exerted by these restraining articles will stimulate blood circulation in the veins of the legs and prevent stagnation of blood or its reflux in the opposite direction.
Why use compression stockings or tights ?
Wearing compression stockings or tights is recommended in various venous disorders, especially in cases of:
- Varicose veins
- Heavy legs
- Oedema of the lower limbs
- Cramps or calf pain
Medical restraint helps:
- Improve venous return and limit blood stasis
- Reduce dilation of veins
- Reduce venous pressure
- Soothe symptoms such as pain, heaviness, swelling
- Prevent the worsening of venous diseases such as thrombosis
- Accelerate healing after venous surgery
- Prevent the appearance of varicose veinsduring pregnancy
The benefits of medical compression
Numerous clinical studies have demonstrated the positive effects of compression stockings and tights on venous health:
- Increased blood flow velocity
- Improved venous return
- Reduction of blood reflux
- Vein diameter reduction
- Relief from pain and heavy leg sensations
- Faster deflation of ankles and feet
Regular wearing of containment items therefore helps relieve the symptoms of venous insufficiency, varicose veins or heavy legs.

Different types of restraint: socks, stockings, tights
There are 3 main types of restraint items:
- compression socks, covering the ankle and foot
- compression stockings, reaching up to mid-thigh or thigh
- compression tights, covering the entire leg from the foot to the waist
Tights have the advantage of exerting pressure on a larger surface area. They are therefore more indicated in cases of extensive venous damage or significant varicose veins.
stockings may be sufficient for moderate disorders, particularly if the varicose veins are located in the calves. They are also more breathable.
compression socks are an alternative for air travel or athletes.
How to choose your contention class ?
Class 1 for benign circulatory disorders
Class 1, called “light restraint”, exerts a pressure of 10 to 15 mmHg.
It is indicated for prevention, during pregnancy, or to relieve moderate disorders such as slight heavy legs or pain.
Class 2 recommended for chronic venous insufficiency
Class 2, called “medium restraint”, exerts a pressure of 15 to 20 mmHg.
This is the compression class usually recommended in cases of chronic venous insufficiency** with varicose veins, edema, heaviness or cramps.
Class 4 for severe cases of venous insufficiency
Classes 3 and 4, called “strong restraint”, exert a pressure greater than 25 mmHg.
They are reserved for severe cases of venous insufficiency with ulcers or after surgery. Class 4 exerts a very strong pressure of more than 36 mmHg.

Also read: Wear your tights with or without underwear ?
How to put on your compression stockings or tights correctly ?
How to put on support stockings: the steps
For optimal effect, it is recommended to put on your compression stockings in a lying position:
- Lie on your back with your leg straight
- Roll up the bottom inside out to the tip of the foot
- Slip your foot into the stocking then unroll it over your leg
- Pull the bottom upwards to avoid creases, smoothing the skin with your hand
- Check that the bottom is in place correctly and that there are no creases
Tips for easily putting on your compression tights
To put on your medical tights, some tips:
- Choose high-waisted tights, easier to put on
- Use a rigid plastic pantyhose insert
- Sprinkle the legs and inside of the tights with talc
- Put on the tights in a seated position, one leg after the other
- Gently pull the tights upwards to smooth the skin
Putting on compression stockings and tights is an essential step to guarantee their effectiveness. Take the time to position the garment correctly and gently smooth the skin, without exerting excessive traction.
— Geoffrey, Founder of The Oversized Hoodie®
Precautions to take when wearing compression stockings or tights
Can we put socks on top of support stockings ?
No, it is better to avoid wearing classic socks over your compression stockings. This could reduce their effectiveness by reducing the pressure exerted on the leg.
Should you wear your compression stockings or tights every day
Yes, it is recommended to wear containment items (stockings, tights, socks) every day to fully benefit from their benefits on blood circulation in the legs.
Regular, daily use allows:
- Maintain effective venous compression
- Limit blood stasis and worsening of varicose veins
- Prevent the appearance of edema of the ankles and feet
It is therefore important to wear your medical restraint every day, ideally from the moment you wake up and throughout the day. However, removing stockings or tights in the evening allows the skin to breathe during the night.

Also read: Tights or stockings ?
The importance of choosing between stockings and tights in summer
In summer, the heat can make wearing stockings or tights unpleasant. Here are some tips for staying comfortable:
- Prefer compression stockings, more breathable than tights
- Choose light materials like cotton for more freshness
- Opt for stockings open to the toes for better ventilation
- Refresh your legs with cold water before putting on the stockings
- Do not hesitate to alternate stockings and tights depending on the situation
However, it is not recommended to completely stop wearing venous compression during the summer, at the risk of worsening venous insufficiency.
Also read: Which tights to wear in summer ?
Stockings and tights for pregnant women
medical compression stockings and tights are particularly recommended for pregnant women, who are exposed to a greater risk of venous disorders.
In fact, pregnancy is accompanied by hormonal changes and an increase in blood volume, which can cause:
- Heavy legs
- From water retention and edema of the ankles/feet
- The appearance of varicose veins
- pain and cramps in the calves
Preventative wearing of containment stockings or tights from the 1st trimester allows:
- Improve blood circulation in the legs
- Limit the dilation of veins under the effect of hormones
- Reduce ankle swelling and the risk of phlebitis
It is recommended to choose class 1 restraint (light) adapted to the future morphology of the pregnancy.
Also read: Why do my tights itch ?
Treat varicose veins with compression stockings or tights
Medical compression is an integral part of the treatment of varicose veins, in addition to other therapies.
Daily wearing stockings or tights allows you to:
- Reduce the dilation of the veins
- Reduce venous stasis
- Improve venous return
- Soothe symptoms such as pain, heaviness, itching
It is recommended to wear a class 2 retainer in case of uncomplicated varicose veins.
In the event of severe varicose veins with risk of complications, class 3 restraint may be prescribed.
Compression items should be worn daily and replaced every 3 to 6 months.
Relieve heavy legs thanks to medical compression
Heavy legs are a common symptom of venous insufficiency, often associated with edema, pain, cramps or varicose veins.
Medical restraint helps:
- Stimulate blood circulation
- Improve venous return
- Reduce blood stasis
By exerting gentle pressure on the tissues, compression stockings and tights provide rapid relief from the sensation of heavy legs.
A class 1 or 2 restraint is generally sufficient to treat this symptom. The effects are visible from the first days of wearing.
Alternatives to compression stockings or tights
What other devices to improve blood circulation ?
In addition to compression stockings and tights, other alternatives exist:
- The elastic bands to wrap around the leg
- compression socks covering ankle and foot
- The pneumatic compression devices by pressure/depression
- Stockings or tights with decreasing pressure
- The anticirculatory stockings exerting pressure on the heel/ankle
These medical devices can be interesting options depending on the case.
How to replace compression stockings or tights ?
It is not recommended to completely stop wearing venous compression.
Some tips to reduce discomfort:
- Alternate stockings and tights depending on the activities
- Choose breathable materials (cotton) and suitable sizes
- Refresh your legs with cold water before putting them on
- Massage your legs with venotonic creams
A venolymphatic gymnastics can also stimulate blood circulation as a complement.

Also read: Where to buy the best Fleece Lined Tights transparent ?
Medical restraint in the face of phlebitis
Phlebitis is an inflammation of a vein, often in the legs, which can lead to the formation of a blood clot.
In the acute phase, rest and anticoagulants are essential. Wearing compression stockings is therefore contraindicated.
On the other hand, in a second step, restraint helps to:
- Prevent the risk of recurrence
- Promote blood circulation
- Avoiding post-phlebitic syndrome
A progressive restraint must be put in place according to medical advice.
Effects of compression stockings or tights on tingling
The tingling in the legs can be linked to:
- Poor blood circulation
- A compression of a nerve or nerve root
By stimulating venous circulation, medical restraint articles generally help to relieve this symptomatology.
It is however imperative to consult a doctor in the event of severe or persistent tingling, which may require additional examinations.
How to take care of your tights or support stockings ?
To prolong the effectiveness of compression articles and ensure good hygiene, some maintenance tips:
- Hand wash in lukewarm water, with a mild soap or shampoo
- Avoid softeners which reduce pressure
- Dry flat, without twisting
- Store flat or rolled up without folding
- Renew your retainer every 3 to 6 months depending on wear
- Check regularly for the absence of hole or thread pulled
If well maintained, medical compression stockings and tights generally last 3 to 6 months on average before losing their effectiveness.
At The Oversized Hoodie®, we recommend that our customers always wash their restraints by hand and dry them flat, without exposing them to high temperatures. Proper maintenance extends the life of these medical devices.
— Geoffrey, Founder of The Oversized Hoodie®
Also read: How to Maintain Your Polar Tights ?
Conclusion
In conclusion, compression stockings and tights constitute effective medical devices for treating many venous disorders.
Their daily use, at the appropriate compression class, allows lasting improvement of blood circulation and relief of symptoms. The choice between stockings and tights will depend on preference and lifestyle, with tights offering a greater surface area for compression.
Whatever the model, it is essential to ensure rigorous donning and maintenance to optimize the benefits of these containment articles on the venous health.
| Type of Restraint | Compression Zone | Instructions | Compression Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compression stockings | Mid-thigh or thigh | Venous insufficiency, varicose veins, heavy legs, edema | Class 1, 2, 3/4 |
| Compression tights | Foot at the waist | Extensive venous disorders, significant varicose veins | Class 1, 2, 3/4 |
| Compression socks | Foot and ankle | Local compression | Class 1, 2, 3/4 |
FAQ
What is the difference between support stockings and support socks ?
The compression stockings go up to the mid-thigh or thigh and exert pressure along the entire length of the leg.compression socks only cover the foot and ankle, for local compression.
What are compression stockings used for ?
The compression stockings exert pressure which stimulates blood circulation in the legs. They treat venous insufficiency, varicose veins, heavy legs, edema.
Is it good to wear support stockings every day ?
Yes, it is recommended to wear your contention stockings or tights daily to take full advantage of their venous benefits.
Why wear compression tights ?
compression tights have the advantage of exerting compression over a large surface area. They are indicated in cases of extensive venous disorders or significant varicose veins.
When not to wear support stockings ?
compression stockings should be avoided in cases of acute phlebitis, severe arteriopathy, decompensated heart failure or progressive dermatosis.
Compression stockings for how long per day ?
compression stockings or tights should be worn as long as possible during the day, ideally from the morning after washing until bedtime.
What to replace compression stockings with ?
Other compression devices exist (bands, socks, pneumatic compression, etc.) but it is not recommended to completely stop wearing compression without medical advice.
Sources
[1] "Compression therapy for treating stage I and II (Widmer) post‐thrombotic syndrome - Kolbach, DN - 2003", Cochrane Library
[2] "Evaluation report on medical compression devices for individual use", High Authority of Health
[3] "Document on medical compression", CNRS







